Autosomal trisomies

| Condition | HCG | PAPP-A | AFP | Inhibin A | Nuchal translucency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trisomy 21 | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Trisomy 18 | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | normal | ↑↑ |
| Trisomy 13 | ↓ | ↓ | normal | normal | ↑ |
Mnemonic
- Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
- Drinking age (21).
- Markers for Down syndrome are hi up: ↑ hCG, ↑ inhibin.
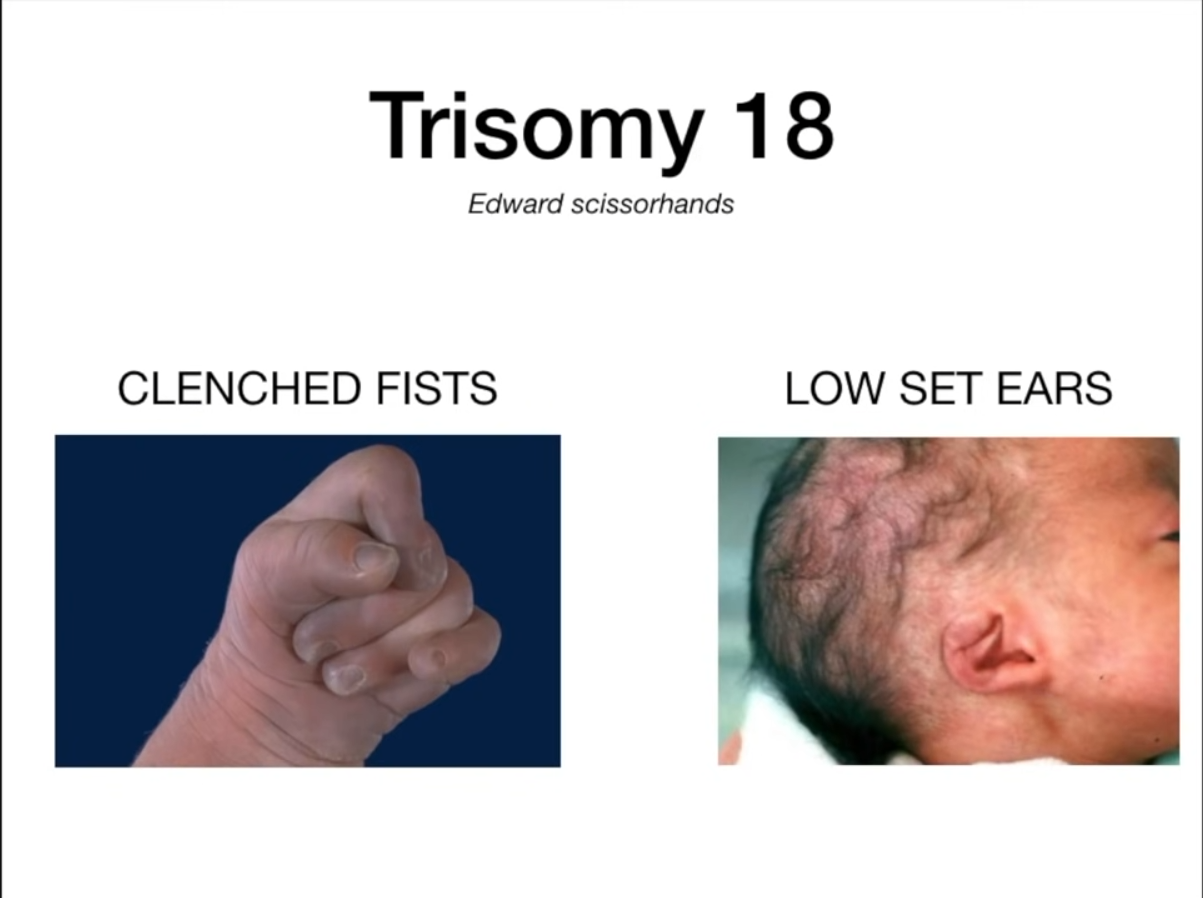
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)
- Election age (18).
- In Edwards syndrome, every prenatal screening marker decreases.
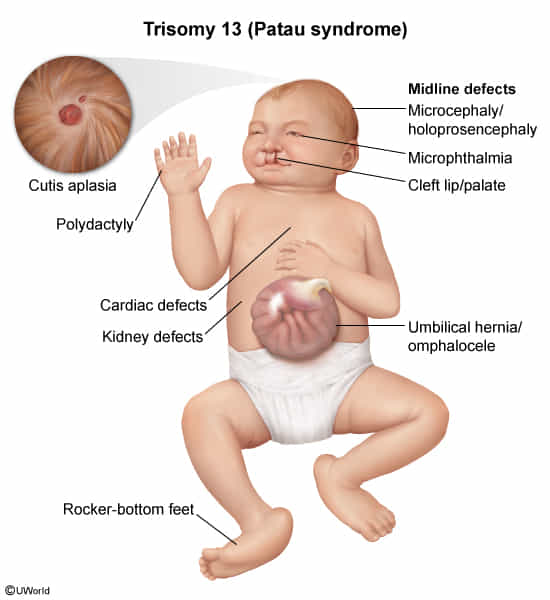
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
- Puberty at age 13.
Tip
-
Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein-A (PAPP-A): A large glycoprotein produced by the placenta, involved in regulating the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system, which is important for placental formation, fetal growth, and trophoblast invasion. Low levels are associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes.
-
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome): The key is an abnormally functioning placenta.
- ↑ hCG & ↑ Inhibin A: The placenta overproduces these hormones, reflecting abnormal syncytiotrophoblast function. It's an "inefficient but overactive" placenta.
- ↓ AFP: The fetal liver is less mature, leading to decreased production.
- ↓ PAPP-A: Reflects early placental dysfunction.
-
Trisomy 18 (Edwards) & Trisomy 13 (Patau): The key is severe placental failure and profound fetal defects.
- ↓↓ hCG & ↓↓ PAPP-A: Both are severely decreased due to a small, profoundly dysfunctional placenta that is failing.
- AFP (Trisomy 18 ↓, Trisomy 13 Normal/↑): AFP is low in Trisomy 18 due to severe growth restriction. It can be normal or high in Trisomy 13 due to associated defects like omphalocele.
Down syndrome
Edwards syndrome

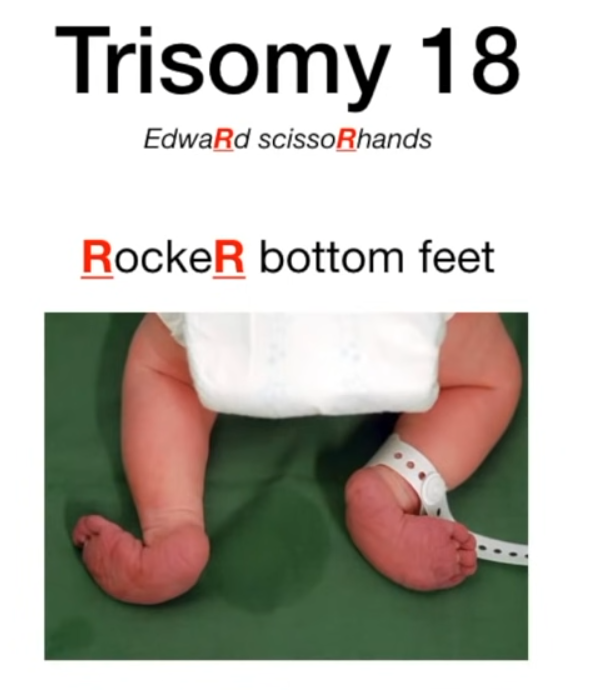
- Rocker-bottom feet can also be found in Patau syndrome.
- This is a rocking chair

- This is a rocking chair
Patau syndrome
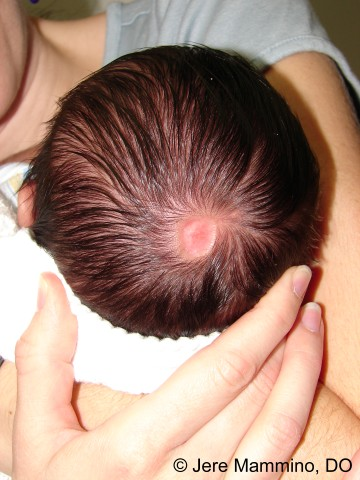
- Aplasia cutis congenita: congenital absence of skin; most commonly scalp lesions with a punched-out appearance that may extend to the bone or the dura